America has diligently added calcium to its drinking water for the last thirty years to counteract hard water. It is estimated that over 80% of Americans are consuming more calcium than is recommended for their age. The trend has increased in recent years in an effort to prevent kidney stones.
Those who drink softened water may be getting more than just the calcium that the body needs. Recent studies have shown that this practice is counterproductive for many. The focus should be on the quality of the drinking water itself, not adding something to it.
The most common methods to remove calcium from water are by using filtration and ion exchange. Filters can reduce the amount of calcium in the water, but they may not remove it completely. Ion exchange uses a chemical process that replaces calcium with hydrogen ions. It’s a more permanent solution, but it’s expensive and needs to be replaced every few years.
Why You Need to Get Rid of Calcium in Your Water
Too much calcium can be toxic and can build up over time, becoming deadly poison. Calcium also leaches magnesium, another essential element for health. Calcium supplements may already be too much for you, but calcium-based baking soda is likely to be even more dangerous.
Here are 11 reasons why you should get rid of the calcium, which can be found in your water, and why it is a problem:
1) Kidney Stones – The most common cause of kidney stone disease is excess dietary intake of oxalate-rich foods. It causes painful urination when these substances lodge in the urinary tract and form crystals. Calcium deposits in the urine more readily when consumed in excess.
2) High Blood Pressure – High blood pressure is caused by excess calcium in the body. When this happens, it blocks the arteries to your heart, increasing your risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
3) Atherosclerosis – Calcium can build up in the arteries of your heart and cause them to narrow, which leads to heart disease.
4) Osteoarthritis – Excess calcium intake increases the risk of osteoarthritis by causing inflammation in the joints.
5) High Cholesterol Levels – Excess calcium deposits around the artery walls cause a hard plaque prone to rupture and blockages.
6) Gallstones – Calcium makes the bile less acidic, so the stones precipitate out of solution and get stuck in the gallbladder or intestines.
7) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Too much calcium increases your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis because it can lead to inflammation of your joints. Furthermore, it causes cartilage and bone tissue to erode, as well as other inflammatory processes.
8) Osteoporosis – Calcium deficiency leads to osteoporosis, in which brittle bones break or fracture more easily due to excessive pressure.
9) Depression – Calcium intake can increase stress hormones, which affect your mood.
10) Cancer – Excess calcium intake can cause cancer by increasing your risk of forming cancerous tumors, but that is not all! It also causes inflammation which makes you more susceptible to cancer.
11) Heart Disease – Calcium intake leads to hardening and narrowing arteries, causing heart attacks and strokes.
Symptoms of Calcium Buildup and How to Spot Them
Identifying symptoms of high calcium levels in water can save you from extensive water damage to your plumbing.
But if you are unsure about the symptoms, here are some signs that may help you identify high levels of water containing calcium:
- Water takes longer to heat up
- Water has a salty or yeasty taste
- Noticeable white buildup around pipes and the faucet.
Water Filtering to Remove the Calcium From the Water
Water is a vital part of our lives. It helps our cells function properly and transports nutrients to all the parts of the body. So, it’s important to make sure that we are drinking enough water every day.
Consuming too much hard water can lead to health problems due to its calcium and other minerals. Before you switch to bottled water, there are systems on the market that remove these minerals.
Several Types Of Filters For Removing Calcium And Other Minerals From Drinking Water
1) Reverse Osmosis
This filter removes 99% of contaminants, including heavy metals, pesticides, herbicides, pharmaceuticals, bacteria, viruses, arsenic, mercury, nitrates, radon gas, radioactive materials, and much more.
The RO filter uses polyamide or cellulose acetate fibers to separate the contaminants from the clean water. They have been proven effective at reducing the amount of harmful elements present in tap water.
2) Distillation
This type of filter removes up to 99% of contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, herbicides, pharmaceuticals, bacteria, and viruses. Distillers are the most efficient way to purify water. Combining boiling and condensation methods can be automated or done manually.
3) Ion Exchange
This is a reverse osmosis (RO) system in which an ion exchange resin removes minerals and other contaminants from water. Activated carbon, diatomaceous earth, zeolite, or manganese oxides are used for ion exchange resins. An ion exchange system offers higher purity than RO systems and lower energy consumption.
4) Water softeners: What do they do?
You can use a water softener to get rid of hardness minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, from the tap water.
The process starts with incoming hard water moving through a tank of salt or saltwater. The salt or saltwater bonds with the hardness minerals to form a substance called “salt cake.” This substance is then drained away and flushed down the drain. The clean softened water goes on to fill your home’s pipes, faucets, and appliances.
How Do You Know When Water is Hard?
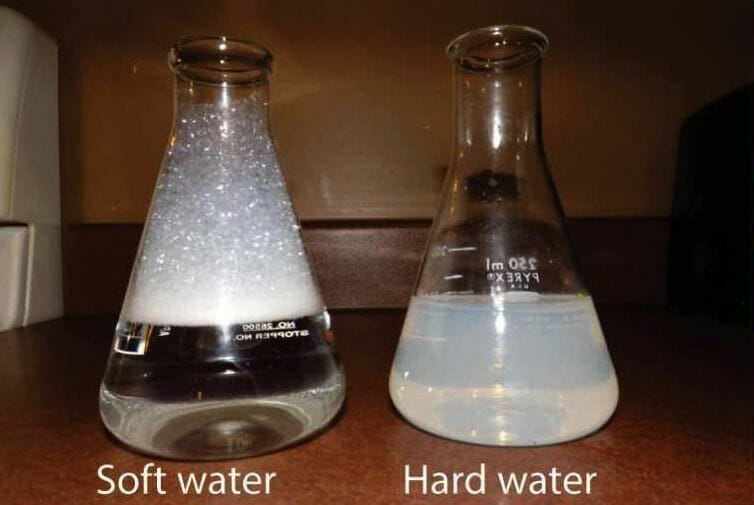

Several signs can help you determine whether water is hard or not. For example, when hard water evaporates, it leaves some residue of calcium and some other minerals that will not evaporate alongside. Some other quick-fire indications you will find at home include the following:
- Rusty stains on kitchen appliances like sink, water tap, around the drainage, etc.
- Limescale reactions from mineral deposits on bathroom plumbings.
- Dryness of the hair.
- Hair fall.
- Hair removal.
- Extreme dullness of skin color and texture.
- The lack of shine on clothes when you use hard water to wash, etc.
If you notice these signs in your home or on your body, it means you’re using hard water. To make your water supply more suitable (both for household and body use), the first step is to check the level of hardness of the water. You can easily measure water hardness using a TDS meter. Some other popular indicators of hard water include the presence of Limescale.
How to Remove Calcium From Water
There is a lineup of numerous techniques to reduce or get rid of calcium from hard water. Some of the best practices include:
- Using conventional water softeners
- Ion exchange
- Reverse osmosis
- Combine scale removal filters
- Scale inhibition filters
- Use of magnetic, Ionization, and catalytic devices, etc.
Filtering and Purifying Drinking Water
It is essential to filter and purify drinking water before drinking. Purification can help to reduce water hardness in drinking water. There are various ways through which you can purify water for Drinking. Some of the best practices include:
- Using a reverse osmosis water purifier
- Boiling
- Using a water filter
Boiling Drinking Water to Make It Soft enough for Drinking
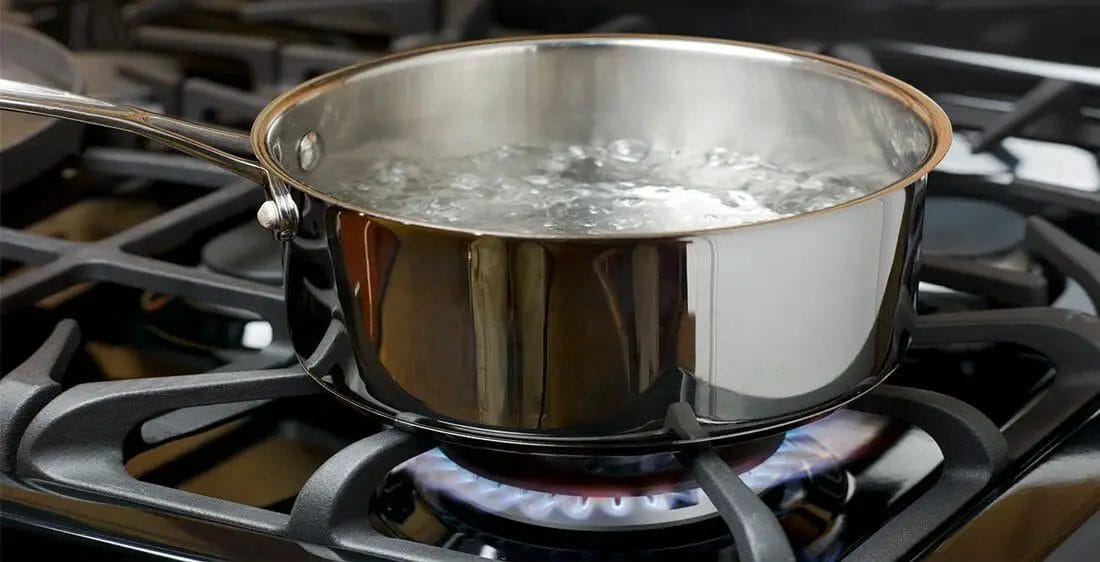

Boiling is the most common and most basic method for purifying drinking water. The process is also quite simple.
- Boil the quantity of water you need
- The water should continue to boil for at least ten to fifteen minutes
- Allow the water to cool afterward before drinking
When you boil water, you also remove some of the mineral deposits that make it hard. Some calcium mineral deposits, like carbonate hardness (which constitute water hardness), are easily gotten rid of in the process. However, it doesn’t eliminate everything.The carbonate hardness that can be gotten rid of by boiling includes calcium hydroxide, calcium bicarbonate, and calcium carbonate.
What are the Best Reusable Filters for Removing Calcium From Water?
Water softeners mean that it is unlikely that you will need to buy the best reusable filters for removing calcium from the water.
However, if you don’t have a water softener or want to buy one, this article is for you. Water with a lot of calcium can leave a bad taste and cause dishes to look cloudy. With these filters, you can remove calcium from the water and have your tap water taste as pure distilled water should.
Why is calcium bad for your pipes, and how does it get in your water?
You might be wondering how calcium can get into your water. You should know that there are numerous ways to enter your pipes and become a problem.
Calcium and other impurities can come from various sources, including:
- Techniques like filtration and disinfection introduce chemicals like chlorine and calcium hydroxide into water.
- The insoluble calcium hydroxide reacts with the hard water to create hard scale deposits inside pipes.
- Companies treat water with chemical additives to disinfect it before delivering it to you, which also reacts with the calcium in the water, causing hard deposits.
- Hardening mineral tap water by adding a type of salt
How to Recognize a Calcium Build-Up Coming From Your Pipes
The water in your home may have a white or yellowish tint, it may be time to schedule plumbing service.
Common signs of a calcium buildup are discoloration in the water and decreased water pressure. Another visual cues are the formation of scale on pipes or faucets.
How to remove calcium from water pipes
The problem is that calcium can cause pipes to clog, leading to low water pressure or no water flow at all.
For ridding yourself of hard water:
Use baking soda and vinegar.
Add the two ingredients to a bowl and mix them until you get a paste-like consistency.
Scrub it on every part of the item where hard water has accumulated.
Let it stay for five minutes before washing it off to remove all baking soda and vinegar traces.
Boil the mixture in a pot for five minutes before scrubbing it onto surfaces with hard water accumulation. The heat will help release any remaining deposits while also disinfecting the surface.
How to remove calcium from water faucet
Here’s how to get rid of calcium buildup on faucets.
- To prevent this problem, use only distilled water whenever possible.
- Distilled water has no mineral content at all.
- Use bottled water instead of tap water.
- You should not make ice cream with tap water!
- Tap water often contains too much salt.
- Salt makes ice cream melt faster than normal.
- Using tap water will make your ice cream melt before it gets cold enough to eat.
- Remove Hardness From Drinking Water With A Reverse Osmosis System
How to remove calcium from well water
Calcium is prevalent in well water. If it is not removed, it can cause problems like clogging pipes and making the water taste bad. This article will discuss two ways of removing calcium from well water.
The first way is to use a filter cartridge or a filter system. Changing the pH level of the water allows calcium to dissolve and be removed by sedimentation. Another option is to exchange the minerals in the pipes using an ion exchange system. Both types of systems need regular maintenance.
Removing Calcium from Well Water Using Filtering Systems
A filtering system uses a series of cartridges or membranes to remove impurities from the water. A typical filtering system consists of the pre-filter, the main filter, and the post-filter. Pre-filters usually consist of coarse sand or gravel.
They help reduce large particles from entering the main filter. Main filters contain granular activated carbon. These filters trap smaller contaminants, including bacteria and viruses. Post-filters are used after the main filter to cleanse the water further.
A filtration system must be maintained. Regularly cleaning out the pre-filter helps prevent the buildup of debris inside the unit. Cleaning the main filter reduces the amount of time required to change its media. Finally, replacing the post-filter every six months prevents contamination of the water supply.
How to remove calcium from pool water
To begin with, you need to understand the nature of your pool water. The salt chlorinator won’t remove calcium from saltwater since it can’t remove it.
If you have a regular pool, the first thing to do is find out what kind of calcium you’re dealing with. There are three types: hardness, total dissolved solids (TDS), and total alkalinity (TA). To calculate how much it costs you, divide the cost per ton by 12 months and divide that number by 2,000 gallons (the average size of a swimming pool).
Calcium cannot be removed from saltwater pools, but it can be reduced if your TDS or TA levels are high. For example, if your TDS is 1,500 ppm and your TA is 500 ppm, you would pay $0.50/ton, divided by 2,000 gallons 0.025 cents/gal.
How to remove calcium deposits from the refrigerator water dispenser
Calcium deposits can be removed from water dispensers using chemical cleaners.
A mineral buildup is commonly responsible for hard-to-remove calcium deposits from refrigerator water dispensers. This can happen after a long period, and it often happens to those who do not use filtered water in their fridge.
Whether you have hard water or a naturally high calcium supply in your home is important to determine. You will need to take care of hard water before you can proceed with anything else. If you’re not sure how much calcium the supply has, the best way to figure that out is by contacting your local authorities.
To remove the deposit, one would need two cups of unscented dish soap and one quart of warm water. The next step would entail pouring the solution into the reservoir where the water comes out. Rinse the area with tap water after letting the mixture sit for about five minutes. Afterward, rinse off any remaining residue using plain water.
Getting rid of Calcium Deposits on Your Shower Head
Hard water can cause problems in your home, including clogged drains, pipes, and faucets. Additionally, it can cause issues with your plumbing fixtures, like showerheads.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s time to call a plumber. Reverse osmosis filters work well to reduce hardness in household water supplies. For homeowners who want to improve the quality of their water, they are an excellent choice.
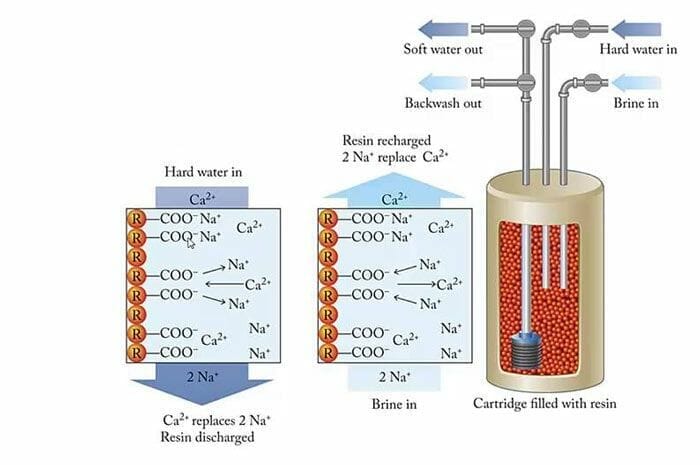
How do ion exchange and filtration work for removing calcium from water?
Ion exchange and filtration are used to remove calcium from the water. The process involves using an exchange resin that has been saturated with sodium hydroxide (NaOH). This resin will then be placed in the water being treated.
When the resin is exposed to the water, it will release sodium ions into the water. These sodium ions will replace the calcium ions on the resin. Having removed all calcium ions from the resin, regenerating the resin is necessary to continue using it.
Acid solutions are used to regenerate resin to reabsorb sodium ions. After this step, the resin may be reused many times until it becomes exhausted.
How to Test for High Levels of Calcium in the Home
The best way to test for high calcium levels in the home is to take a sample of the water from your faucet.
The recommended range for calcium in drinking water is 120-400 mg/L.
Common sources of calcium in the water
We can find calcium in some vegetables, dairy products, and nuts. However, we need to consider that calcium in these sources is not as high as in milk.
A lot of people think that the calcium we get from drinking water is enough to be healthy. But it’s not possible because one cup of milk contains about 300 mg while a glass of water only has 14mg. Drinking water alone cannot provide all our daily calcium needs, and we need to find an alternative source of it.
Best Methods for Removing Calcium and other Metals from your Drinking Water
There are many methods of removing minerals from water. Some are more effective than others, but finding the best method for your needs is important.
Among the most common methods of removing minerals from drinking water is boiling. If your tap water or distilled water contains magnesium or other metals, boil it for at least 10 minutes.
Use a filter designed specifically to remove metals from drinking water at home or work. You can buy filters on Amazon or any other store, but some popular brands are Brita, ZeroWater, and PUR.
Monitoring and inspecting for calcium
Calcium is usually found in small amounts in household plumbing systems. Calcium shouldn’t accumulate in your house unless something goes wrong during installation.
However, when looking for signs of excessive calcium buildup, look out for:
- Hard water stains around sinks, tubs, toilets, etc.
- Stains on walls, floors, appliances, fixtures, etc.
- Discoloration of pipes drains, etc.
Why is calcium present in water?
Calcium is naturally seen in the water. This may dissolve rocks like limestone, calcite, marble, gypsum, dolomite, apatite and fluorite.
Calcium is a precondition of water hardness as this is found in water as Ca2+ ions. Magnesium is considered as the different hardness.

Calcium can be seen in may construction materials, like cement, concrete and brick lime. This is also present in batteries and is used in plaster like calcium sulfate. The metal is used for thorium and zirconium production.
Calcium is used as blotter in the steal industries, is added to aluminum, lead alloys and copper. Calcium can be extracted sulfur dioxide from the industrial exhaust, or neutralize sulphuric acids prior discharge.
The another use of calcium is calcium hypo chloride for bleach for disinfection, porcelain industries or calcium phosphate, hydroxide, calcium polysulphide, as flocculants in wastewater treatment, calcium fluoride as turbidity agent in the enamel industries, and in UV spectroscopy and raw materials for fluid acid production.
Calcium may be used as removal of sulfur or carbon and iron alloys and iron, for dewatering oil. Limestone is used as paper filler may cause the paper to color whither and in plastics to improve stability.
Calcium sometimes affects the quality of the soil, and different compounds are used in fertilizer. Suppose, CaCl2- or Ca(NO)3 are used in horticulture. Again, Calcium oxide is considered dehydrating molluscicide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about How To Remove Calcium From Water
1. What is calcium, and Why should I Care about Taking it out of My Water?
Water treatment is important to understand if you want to know how to remove hardness from your water. Minerals in the water cause water hardness. These minerals are often calcium and magnesium.
The EPA recommends that people drink 8 glasses of water per day. Hard water can cause health problems because it causes the body to hold onto more calcium than it needs. You can remove calcium from your drinking water in a few ways:
- Using a filter on the tap
- Adding a liquid hydrogen peroxide solution
- Adding hydrogen peroxide tablets
2. What Causes High Calcium Levels in Water?
High calcium levels in water are a common problem for people living in hard water areas. Inorganic calcium dissolved in the water comes from mineral deposits, wells, and surface runoff.
By sending a sample of the water to a lab, you can detect high levels of calcium. Home test kits are also available for this purpose. You will learn about the hardness level in your water and other factors that may affect its quality.
3. Why You Need a One-of-a-Kind Home Remedy to Remove Calcium from Your Drinking Water
The following home remedy is a safe and efficient way to remove calcium from your drinking water:
- Pour 8 ounces of vinegar into a pitcher and fill it up with cold water.
- Add 1 teaspoon of salt to the mixture and stir until dissolved.
- Add the mixture to your faucet at full strength for about 20 seconds.
- Wait for 20 minutes before using the faucet again or refill the pitcher with fresh water and repeat the process if necessary.
4. Is tap water with limescale harmful?
- Limescale is not unhealthy, but it is not healthy either.
- Calcium and magnesium are essential nutrients for our bodies.
- You can get these nutrients from drinking water.
5. Why should calcium carbonate be removed from drinking water?
Hard water can cause serious problems if consumed over long periods.
- It can affect your skin, hair, and utensils.
- Your food may also taste different.
6. How do you know calcium from water needs to be removed?
- Water that is hard is caused by calcium and magnesium concentrations that are too high.
- Pipes and fixtures accumulate calcium and magnesium over time.
- You can remove calcium from the water using a water softener.
7. Does boiling water remove calcium?
Water can be removed from calcium by boiling; however, there are other ways to do it without boiling.
8. How Does Calcium Get Into Water?
- Water contains many minerals, including calcium.
- When water passes through pipes or plumbing systems, calcium builds up inside them.
- This buildup occurs when hard water enters the system.
- If the water supply is made up of hard water, the amount of calcium increases.
9. How do you lower calcium hardness?
Softening water can be achieved by filtration, deionization, distillation, and chemical treatment. Each method works, depending on what type of water source you have. For example, RO removes dissolved solids, which include calcium and magnesium.
Deionization uses electrical charges to separate particles. Distillation separates impurities based on boiling point. Chemical treatments involve adding chemicals to the water to change its properties.
10. Is it bad to have calcium in your water?
Yes, calcium is not good for human health. Calcium concentrations can damage teeth, bones, blood vessels, kidneys, and even the brain. Some experts believe that excessive amounts of calcium may contribute to heart disease.
Calcium-rich foods should be limited, recommends the American Dental Association. Some people prefer low-calorie beverages, like diet soda, because they contain little or no sugar. Others prefer to avoid sugary drinks altogether.
11. Is Kent Water Purifier removing iron, calcium, and magnesium from water?
The Kent water filter removes both calcium and magnesium from drinking water.
12. What are the most common methods to remove calcium from water?
- The most common method to remove calcium from water is by using reverse osmosis.
- Do you need to use both filtration and ion exchange to remove calcium from water?
- Yes, you need to use both filters to remove calcium from your water.
13. Are there any filters that are effective at removing calcium from water?
There are several ways to remove calcium from the water. The most common way is by using reverse osmosis (RO) systems.
14. What are the symptoms of high levels of calcium in water?
The symptoms of high levels of calcium in water include:
- Bloating
- Constipation
- Headaches
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea
- Skin rashes
- Swollen ankles
- Tooth decay
- Weakness
- Weight gain
- Yellow skin/eyes
15. What are the most common methods for removing calcium from water?
The most common method for removing calcium from water is by using reverse osmosis.
16. What are some of the disadvantages of using ion exchange to remove calcium from water?
Ion exchange is not recommended for removing calcium from water because it can cause damage to your pipes.
17. Does boiling water remove calcium from water?
Yes, boiling water removes calcium from the water.
18 Hard Water: Solutions
Too much calcium can cause calcification that shortens the life of several appliances, including your washing machine and dishwasher. Perhaps you have heard about hard water from a friend or family.
19. How can I use it to remove calcium buildup from my water?
White vinegar is very effective in removing calcium buildup from the water.
20. Hard Water: Why do we need to change our water?
The laundry process often creates an acidic solution, which will dissolve the calcium out of the water. The best fix is to install a filter or use vinegar in your laundry. Changing to hard water could be needed if you are having issues with soap bubbles and laundry stains.
21. Hard Water Causes Leaks
The plumbing system is susceptible to injury from hard water. The corrosion can cause leaks, which in turn lead to water damage and disrepair of your plumbing system. Also, clogged drains, leaky pipes, leaking valves, and damaged sprinkler heads come from this.
22. How does sodium bicarbonate work to lower water hardness?
The traditional way to lower the hardness of water is by adding sodium bicarbonate. Rock salt or sodium chloride can also help remove calcium buildup from pipes, but it may harm your bathtub and fixtures. According to www.waterev.com, potassium-based treatment has a much milder effect.
23. Softening agents are used to make the water softer.
The hardness of water is measured by the number of minerals in it. Calcium, magnesium, and sometimes sulfur and iron are found naturally in water. Unlike hard water, calcium softens by having a high affinity with metal ions in soap and enables more effective cleaning at lower temperatures.
You can measure a material’s hardness in parts per million or milligrams per liter. TDS is between 50 and 150 parts per million in typical tap water, while distilled water contains up to 500 mg/L. Most tap water is alkaline, but there are some areas of North America with extremely hard water.
24. What happens when I drink tap water?
The soap scum is the residue left after soap’s salt, or surfactants are rinsed off. Calcium and sodium ions, as well as magnesium and potassium, remain on dishes. Metals in water can cause joint problems if consumed in food preparation or bathing.
25. Ion Exchange Resin
The softening of water is a difficult problem, and water softening has been going on for thousands of years. Several items may be added to soften the water, such as sodium bicarbonate. By chelating calcium from your water into insoluble forms, it can pass through the stomach more easily.
Utility companies install ion exchange resin or pellets below ground level; this device is hooked up directly to the mainline. Another method involves using reverse osmosis systems. RO removes all impurities except those that are too small to go through membranes. However, these devices require large amounts of energy and maintenance costs. They must be replaced every few months depending upon usage.
26. How does calcium hydroxide work?
Calcium hydroxide is a dry powder that can be found at any hardware store. It purifies water by raising the alkalinity of freshwater to prevent rust. If placed in hot water for several hours, calcium hydroxide can be maintained by dissolving the solids in hot water and removing chlorine with an activated carbon filter. This rust remover is used to treat and prepare water, food, or paper.
There are many health-related benefits of washing machine water. Its high calcium content makes it effective at removing limescale from plumbing fixtures and other surfaces.
27. How to remove calcium from the water tank
Two tools can be used to remove calcium from water tanks. One is a chemical called “calcium hypochlorite,” and the other is “calcium chloride.” These chemicals are available in powder, granular and liquid forms.
28. How Much Is Calcium Too Much?
According to the World Health Organization, an adult should consume 700-1000 milligrams. If you are prone to kidney stones, this number may be higher.
Excess calcium can lead to constipation or diarrhea, and stomach pain. It can also interfere with the absorption of other nutrients such as iron and zinc and may affect how well your body stores fat.
If you take more than 500 milligrams of calcium in one sitting, spread it out during the day.
29. How to remove calcium from water heater
To remove calcium from the water heater, mix one tablespoon of vinegar with each gallon of hot water. Wait for about ten minutes before using the water.
30. What is Limescale?
Defining it merely, Limescale is the chalky, white residue left behind from the activity of magnesium, calcium, and other dissolved minerals present in the water. Usually, it forms a hard white crust around the mouth of your bathroom or kitchen taps. The hard coating can prove very tough to get rid of after it has developed.
You can also find Limescale on your kettle, water glasses, coffee maker, cooking pot, frying pan, cutleries, and so on. Statistics show that up to 86% percent of homes in the U.S.A. and over 84% of European houses are plagued by.
31. Is it Bad to Have Limescale in Tap Water?
The major constituents of Limescale in tap water are magnesium and calcium. Contrary to what most people believe, these minerals are not considered to be unhealthy for the body. Limescale, in a reasonable amount, contained in tap water, does not inflict any harmful effects in your system.
Minerals like calcium and magnesium are healthy for the body when consumed moderately. The recommended daily consumption of calcium for the body is between 500 to 1200 milligrams. Magnesium’s daily recommended intake is 300 milligrams.
You can get ten to twenty percent of your body’s recommended daily requirements of calcium if you take up to two liters of water daily. Also, tap water can provide your body with up to one-third of its required magnesium.
Conclusion
The regulations on calcite ion concentration limits in drinking water vary from country to country. Calcium ions in drinking water are limited in some countries but not in others.
Excess calcium levels in your body can lead to a variety of health problems such as kidney stones and high blood pressure.
Ca2+ can be removed from drinking water by installing a 5 stage reverse osmosis water system. Rather than removing Ca2+ from your water, you might want to treat the calcium and install both an In-Line and Hard Water Bulleting System.
Because of the Hard Water Bullet, you won’t need to buy salt, and you won’t waste water because it won’t need regenerating, and you won’t drink chlorinated water.
Sources:
Sarah J. Gregory
352 Hershell Hollow Road
Anaheim, CA 92805






